The transition to a digital society and the restructuring of IT infrastructure
In its DX report, Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry defines digital transformation (DX) as follows.
“DX refers to companies responding to intense change in the business environment by using data and digital technologies to transform their products, services, and business models based on the needs of customers and society while also transforming their business and other processes, organization, and corporate culture to build a competitive advantage.”
To realize this transformation, businesses must have an environment in which they can continue to change dynamically. Businesses must use new technologies such as generative AI and large language models (LLMs), so it is important that they agilely introduce and use new digital technologies. Now it is common for IT and digital infrastructure to be cloud-based. Businesses need to take advantage of IoT and AI technologies to make swift and accurate decisions based on real-world data.
Edge computing for cloud distributed processing
Because of the use of IoT, AI and other new technologies, there are new infrastructure requirements, such real-time capability, decentralized processing, security and cost efficiency. For this reason, the limitations of conventional cloud-centered configurations have started to become apparent. As the shift toward cloud computing unfolds, the need for edge computing is also beginning to rise. Edge computing is a distributed computing concept whereby data is processed and analyzed on IoT devices themselves and/or on computing resources physically located nearby. Because data is not sent to a physically distant cloud but processed and analyzed on the edge of the network, edge computing by its nature can be highly real-time and it helps with load balancing. Compared to the testing (proof of concept) stage, the full-scale commercial implementation of DX involves the explosive growth of the volume of data generated and processed. This is why it is believed that edge computing is becoming more widespread, as, compared to cloud computing, it brings the processing of data closer to the location where data is generated and used.
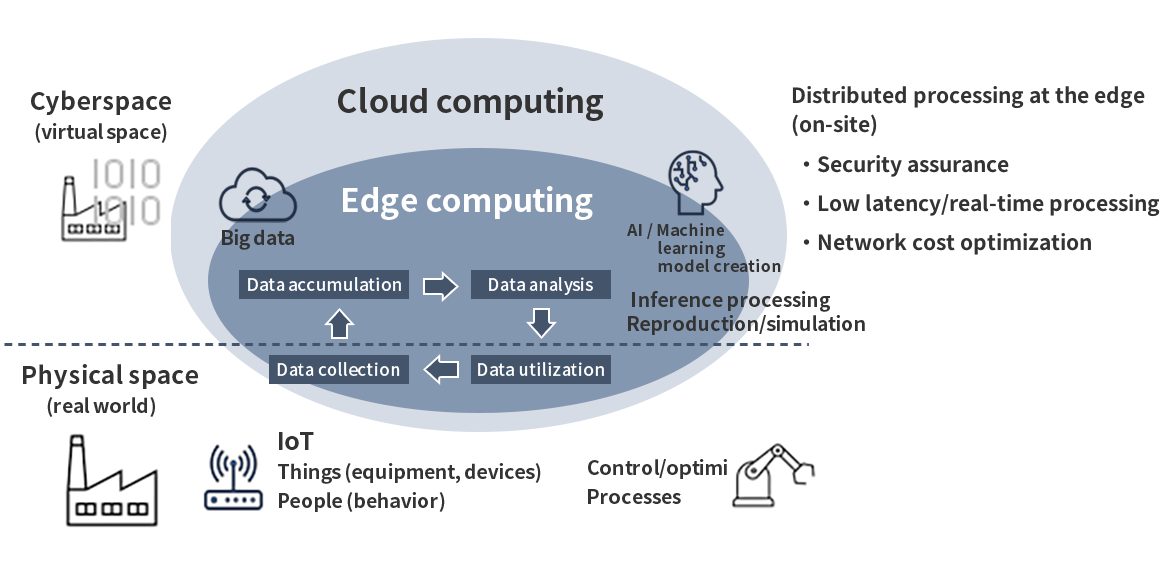
Advantages of using edge computing
(1) Real-time/low-latency data processing
When data is processed in the cloud, it may take from tens of milliseconds to several seconds to send data from an edge device to the cloud and then return the results. The response times of systems may vary. Edge computing supports data processing tasks that require stability and the ability to respond instantaneously, such as device control, image recognition, and AI inference tasks completed by processing data on the edge of the network. Although there are limits to the processing capabilities of IoT and other edge devices, edge servers can be used for large computing tasks to facilitate the real-time processing of production process data without delay.
(2) Reducing network communication costs and cloud usage costs
As IoT technologies continue to evolve and become more widespread, the volume of data transferred across networks will increase. If all of the data were to be collected and processed in the cloud, the volume of data transmitted and processed would grow explosively, which would lead to an explosive increase in the cost of networks. A solution to this problem is bringing edge computing into the mix, alongside cloud-based services, to reduce the network bandwidth that is necessary and, as a result, reduce the cost of networks.
(3) Compliance with internal security rules
When confidential information about production processes and personal information is transferred to or stored on the cloud, there are always security risks, such as the risk of a data breach or an external attack. As a result, many companies have strict security policies, and there are still major psychological hurdles to be overcome to get many companies to use the cloud for commercial purposes.
Using edge computing to process data that involves strict security requirements reduces the risk of a data breach because the data is not sent to the cloud or only a minimum amount of abstracted data is used.
(4) Ensuring business continuity
Edge computing is also useful for BCP (business continuity planning). If all data is stored and processed in the cloud, the failures and disruptions that result in the cloud and networks being down cause business to stop.
If the data necessary for carrying on production processes and business operations are stored on edge servers, then businesses can continue to run even if the cloud goes down. That is, edge computing is an effective part of BCP for business that needs to be restored as a priority and remain in operation in the event of an emergency.